SWAT
SWAT: A Suite of Worst Case Response Time Analysis Tools for Distributed Hard Real-Time Systems.About
For the design of embedded systems that support real-time applications, it is required to guarantee the satisfaction of real-time constraints in any case. For an embedded application that runs repeatedly, the real-time constraint is usually defined by the relative deadline that is the maximum allowable execution delay of an application after being released. The response time of an application is defined as the time interval from the release time to the finish time. After applications are mapped to a candidate architecture, we check the feasibility of the architecture by estimating the worst case response time (WCRT) of an application. Fast estimation enables us to explore the wider design space of architecture selection and application mapping. Accurate estimation avoids over-design to reduce the system cost. However, estimation speed and accuracy are in general incompatible since the accuracy induces higher complexity. Hence various performance estimation techniques are required in the design process.
SWAT (SNU Worst case response time Analysis Tool) is a suite of performance estimation methods to analyze the worst case response time of an application in a distributed real-time embedded system which consists of an arbitrary mixture of preemptive and non-preemptive processing elements, considering execution time variations of tasks, jitter of input arrivals, and scheduling anomaly behavior in a multi-tasking system all together. SWAT consists of various methods that are developed in our laboratory: STBA, HPA, ILP-based analysis, and worst scenario generator. STBA(Scheduling Time Bound Analysis) computes the scheduling time bound of each task by performing scheduling during analysis. STBA produces a much tighter bound of WCRT than compositional approaches while its speed is comparable to compositional approaches. HPA (Hybrid Performance Analysis) is a hybrid technique of the modified response time analysis and the scheduling time bound analysis. Since it does not unroll the application graphs, it shows lower algorithm complexity than STBA. ILP-based analysis finds exact worst case response time using integer linear programming. Speed problem due to its exponential complexity is mitigated by confining the range of ILP variables from the result of STBA or HPA. Worst scenario generator generates a lot of near-worst scenarios for the users to recognize the worst-case behavior.
SWAT was demonstrated in the major conferences such as DAC (Design Automation Conference) and DATE (Design, Automation & Test in Europe). SWAT is still being developed to support various architectures such as multi-core system and shared memory architecture. Corresponding researches are ongoing in our laboratory.
Publication
Demo Videos
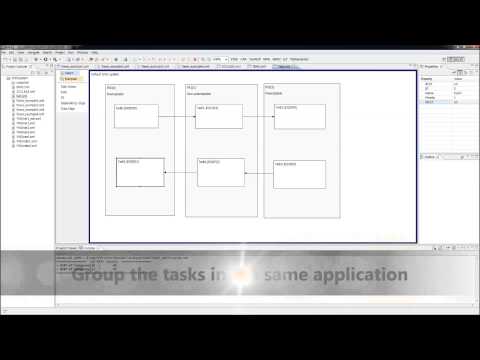
|
DAC 2014 |
| Demo video for S... |
| 2014-10-02 15:30 |
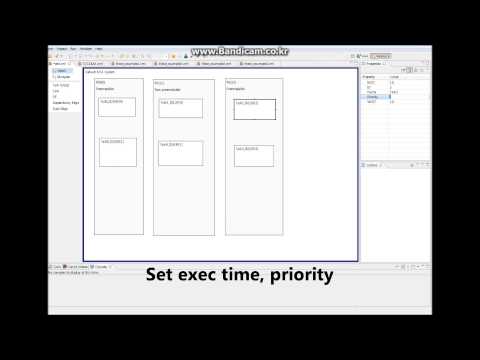
|
DAC 2013 |
| Demo video for S... |
| 2014-10-02 14:30 |
